9 Best Practices for Using AWS Access Analyzer
Maintaining a strong security posture is crucial in today’s digital landscape, and it begins with users. Trusting users with access to sensitive data and company assets is a web of complexity, and one bad apple or security gap can knock all the dominos down.
In fact, Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report noted that 74% of breaches include the human element, either through human error, privilege misuse, social engineering, or stolen credentials.
AWS Access Analyzer was created to address this problem and provide the information you need to achieve the principle of least privilege (PoLP). It plays a vital role in achieving a secure environment by comprehensively analyzing your resource policies, helping you identify any potential security vulnerabilities, and ensuring compliance.
What is the Principle of Least Privilege?
The principle of least privilege states that a user should only have access to the specific data, resources, and applications needed to complete a required task, helping organizations improve their overall security posture and reduce the attack surface.
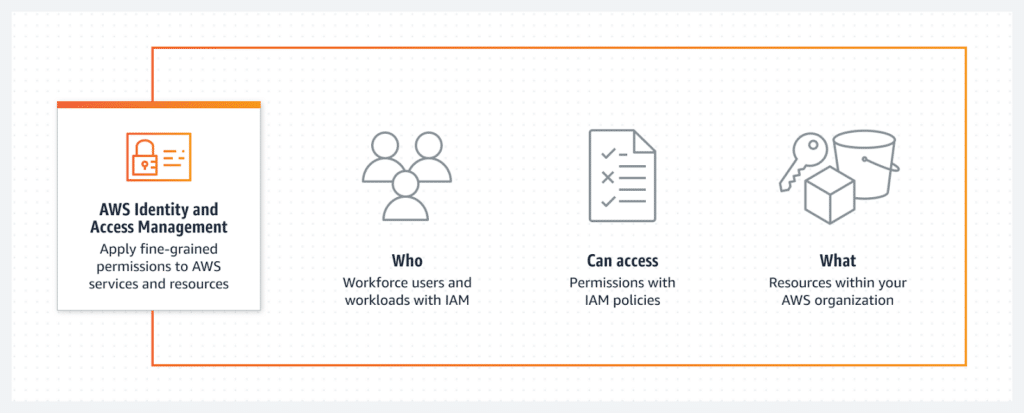
What is AWS IAM Access Analyzer?
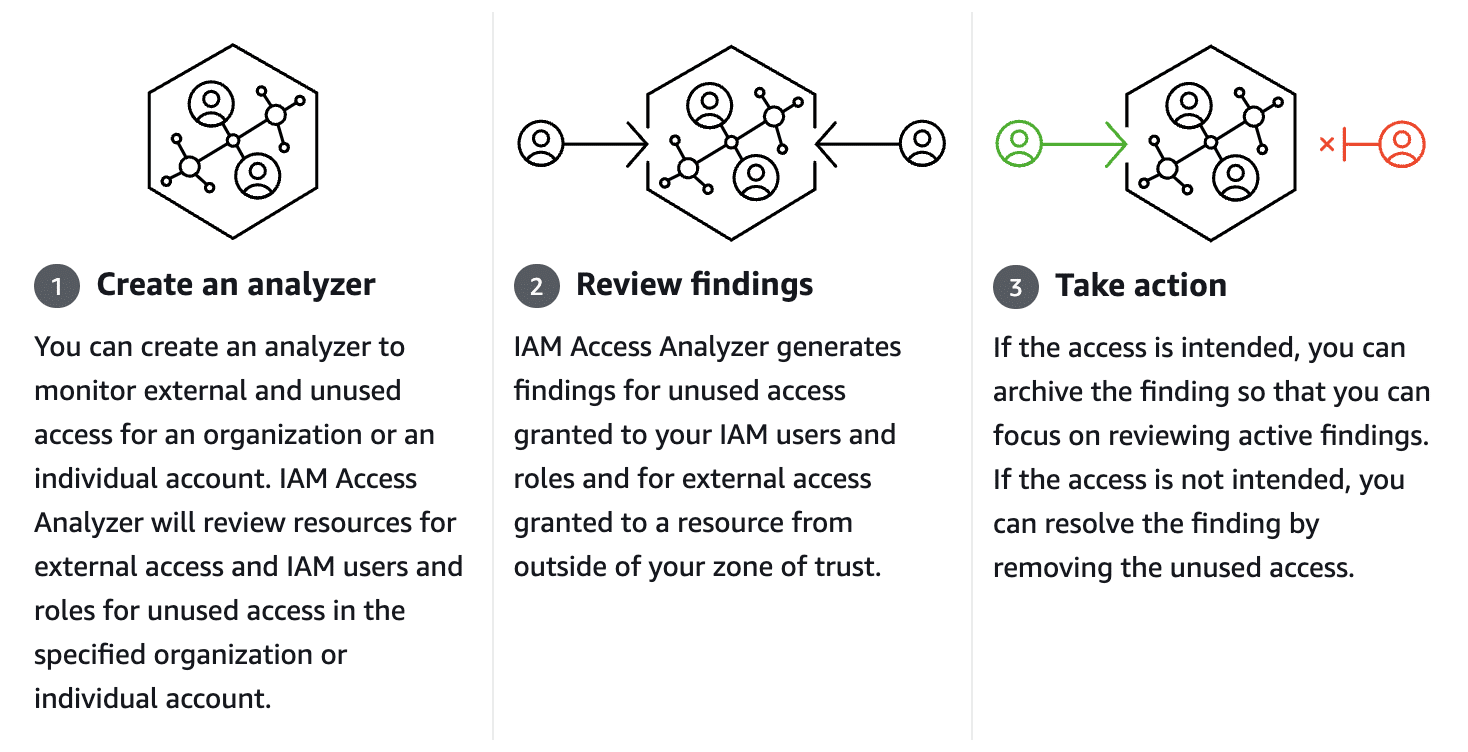
AWS Identity and Access Management Access Analyzer guides you toward least privilege by providing capabilities to set, verify, and refine permissions. IAM Access Analyzer uses provable security to analyze external access and validate that your policies match your specified corporate and data security standards.
What Resource Types Does IAM Access Analyzer Analyze?
IAM Access Analyzer can analyze various resource types within an AWS environment. Some of the key resource types supported by IAM Access Analyzer include:
- Amazon S3 buckets
- Amazon SQS queues
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles
- AWS Lambda Functions and Layers
These are just a few examples of the resource types IAM Access Analyzer can analyze. It is important to note that IAM Access Analyzer continues to expand its support for additional resource types, providing organizations with comprehensive coverage for their AWS environments.
External Access Findings vs Unused Access Findings
Regularly monitoring and managing external access findings and addressing unused access findings will help you maintain a secure AWS environment and minimize the risk of unauthorized access. Let’s look at the difference between external and unused access.
External access
External access findings are critical in identifying potential vulnerabilities caused by access from external entities, such as third-party accounts or entities outside your organization. These findings provide valuable insights into the permissions accessible to entities beyond your immediate control. By analyzing external access findings, you can identify and address potential security risks arising from unintended or unauthorized access.
Unused access
Unused access findings shed light on permissions granted but not utilized, leaving your resources vulnerable to unauthorized access. These findings provide insights into the permissions that are not actively used, indicating potential areas where access can be revoked or tightened.
Why Use AWS IAM Access Analyzer?
With the increasing complexity of cloud environments, it’s essential to have a tool that can identify any security loopholes and policy misconfigurations. AWS Access Analyzer achieves this by providing a detailed analysis of your resource policies, giving you insights into potential vulnerabilities, and helping you remediate them effectively.
You can proactively identify and resolve any overly permissive access policies by leveraging AWS Access Analyzer to protect your sensitive data and help you avoid costly data breaches and compliance violations. With AWS Access Analyzer, you can confidently ensure that your cloud resources are configured securely and in line with your organization’s security best practices.
Key Benefits of AWS Access Analyzer
AWS Access Analyzer offers a range of powerful features and capabilities to help you safeguard your AWS resources.
- Policy Validation: It thoroughly examines your resource policies, including AWS IAM policies, S3 bucket policies, and more. It analyzes these policies against best practices and provides actionable recommendations to improve security and compliance.
- Granular Insights: It provides detailed insights into the specific resource and policy that may expose your environment to potential security risks. This granular level of analysis allows you to quickly identify the root cause of any vulnerabilities and take immediate action.
- Resource Coverage: It supports a wide range of AWS resources, including IAM roles, Amazon S3 buckets, AWS KMS keys, and more. This comprehensive coverage ensures that you can analyze and secure all critical components of your cloud infrastructure.
- Continuous Monitoring: It enables you to continuously monitor your resources for any policy changes or new vulnerabilities. By setting up automated alerts, you can stay informed about potential security risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
9 Best Practices for Using AWS Access Analyzer
Now that you have AWS Access Analyzer up and running, let’s explore how to make the most of its capabilities.
- Define Custom Analyzers
In addition to the default analyzers provided by Access Analyzer, consider creating custom analyzers tailored to your specific needs. Custom analyzers allow you to focus on critical resources and policies, ensuring a more targeted analysis.
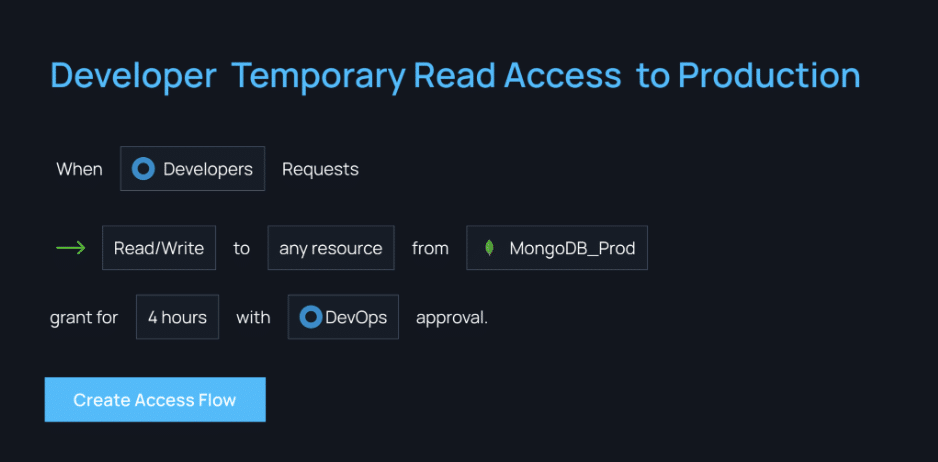
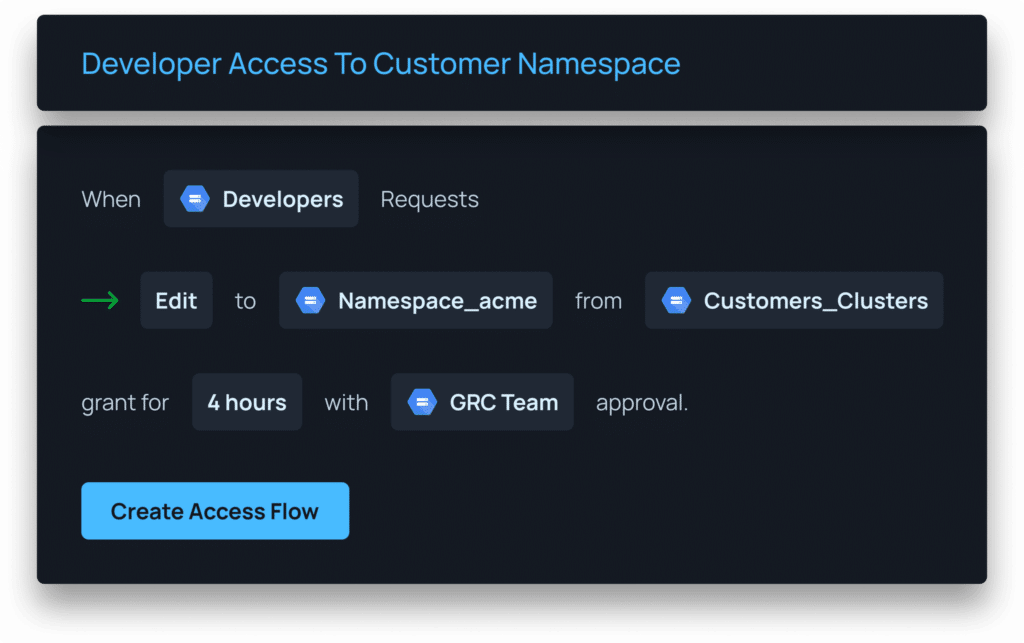
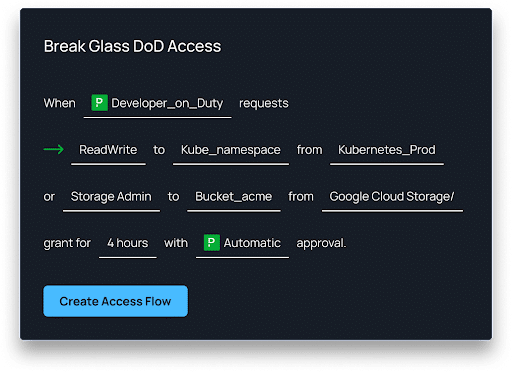
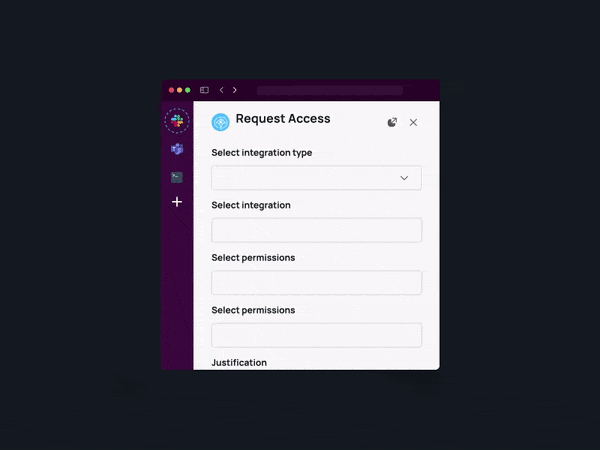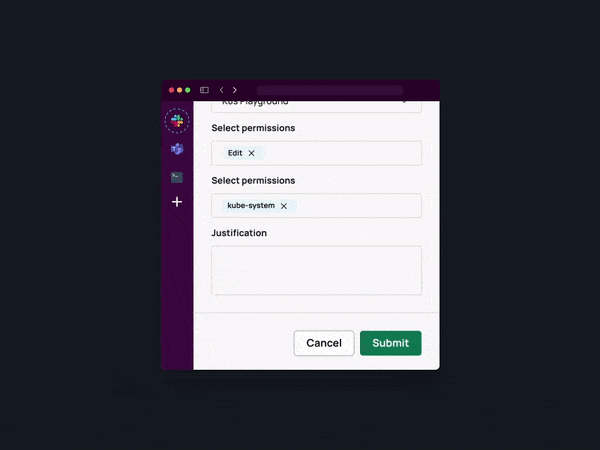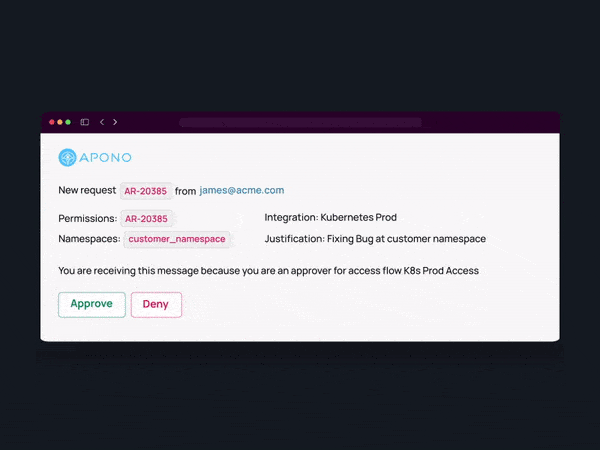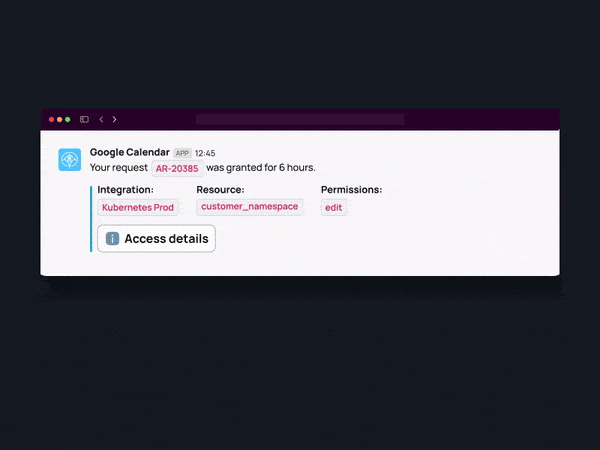
- Utilize Tools for Granular, Just-in-time Access
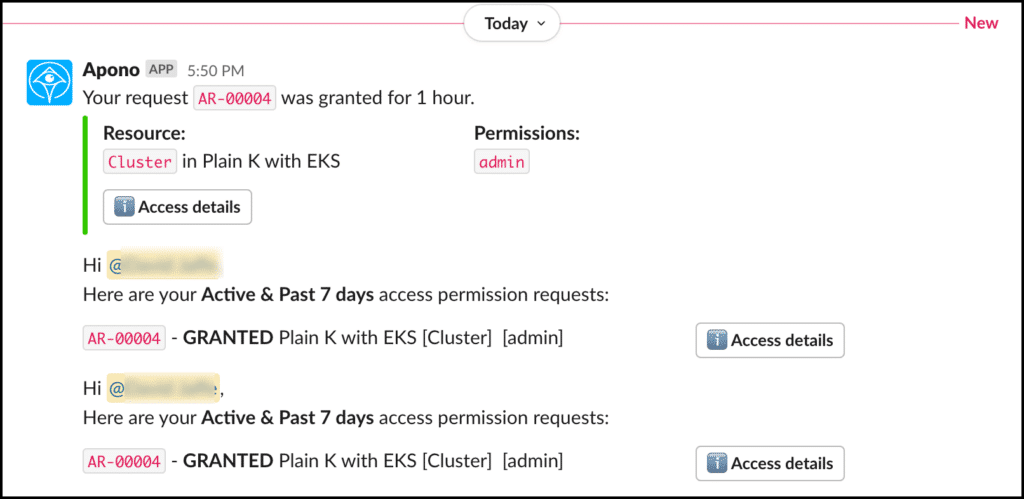
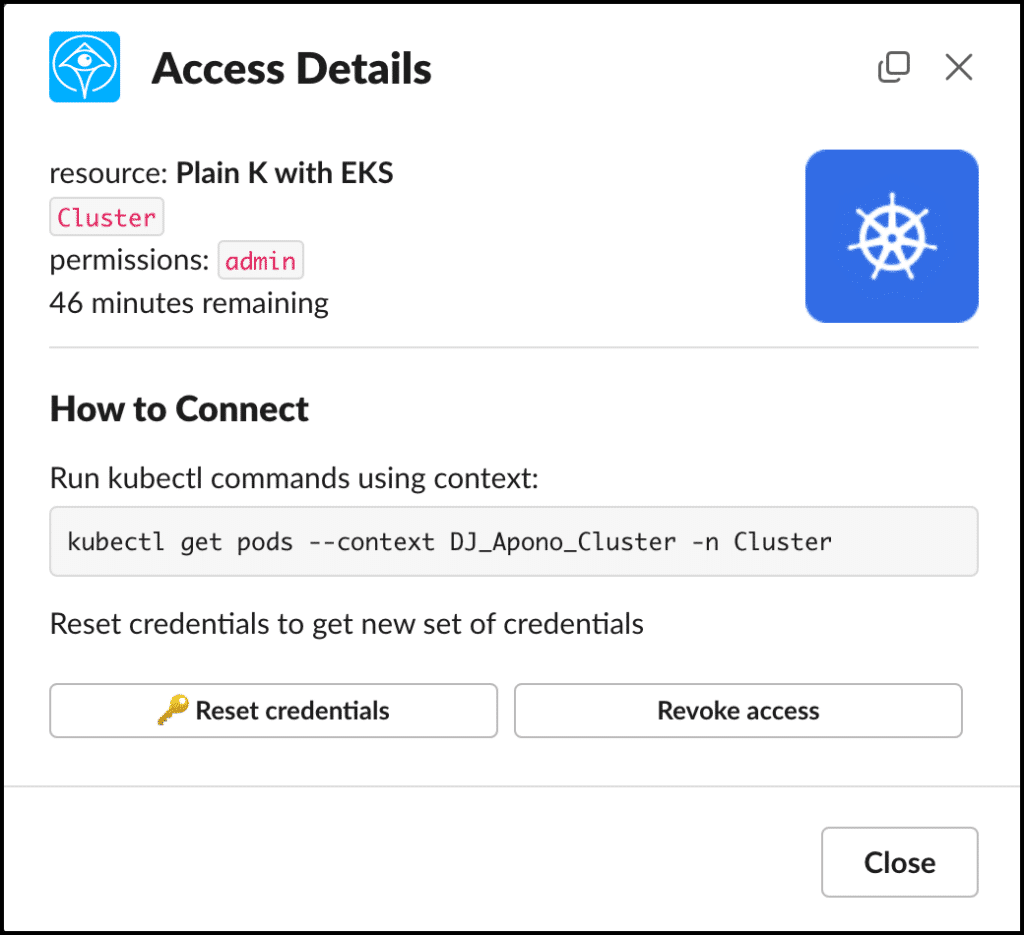
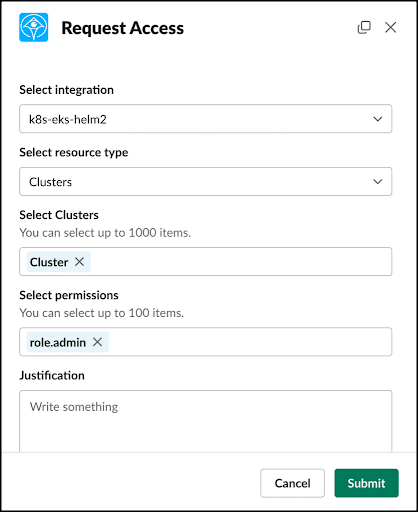
Remove standing privileges quickly and easily. With Apono’s tool, you can provide right-size policies down to any level of granularity needed, all in one centralized location.

- Regularly Review Findings
Make it a routine to review the findings generated by Access Analyzer regularly. This strategy helps you stay updated with any new vulnerabilities or policy changes and allows you to address them promptly.
- Leverage Automated Remediation
Access Analyzer provides automated remediation actions for certain findings. Take advantage of this feature to streamline the remediation process and save time. However, always review the proposed changes before applying them to ensure they align with your security requirements.
- Integrate with AWS Security Hub
AWS Security Hub provides a centralized view of your security posture across multiple AWS accounts. Integrating Access Analyzer with Security Hub allows you to consolidate and streamline your security operations, making it easier to manage and respond to security findings.
- Regularly Run Analyses
Schedule regular analyses with Access Analyzer to continuously monitor your resources for any potential security vulnerabilities. By automating this process, you can maintain a proactive security approach and quickly remediate any identified issues.
- Prioritize Findings
Access Analyzer provides a severity level for each finding. Focus on high-severity findings first, as they pose a greater risk to your security posture. By prioritizing your actions based on severity, you can efficiently allocate your resources and address the most critical vulnerabilities first.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders
Security is a shared responsibility, and involving relevant stakeholders in the remediation process is crucial. Collaborate with your development teams, system administrators, and other stakeholders to ensure that everyone is aware of the findings and actively participates in the remediation efforts, helping promote security awareness.
- Document Remediation Actions
Keep track of the actions taken to remediate the findings generated by Access Analyzer. This documentation helps maintain an audit trail and ensures that you have a record of the steps taken to address any security vulnerabilities.
Use Apono with Access Analyzer
Following the best practices outlined in this article, you can utilize Access Analyzer effectively while using third-party tools to easily create your policies and minimize your attack surface.
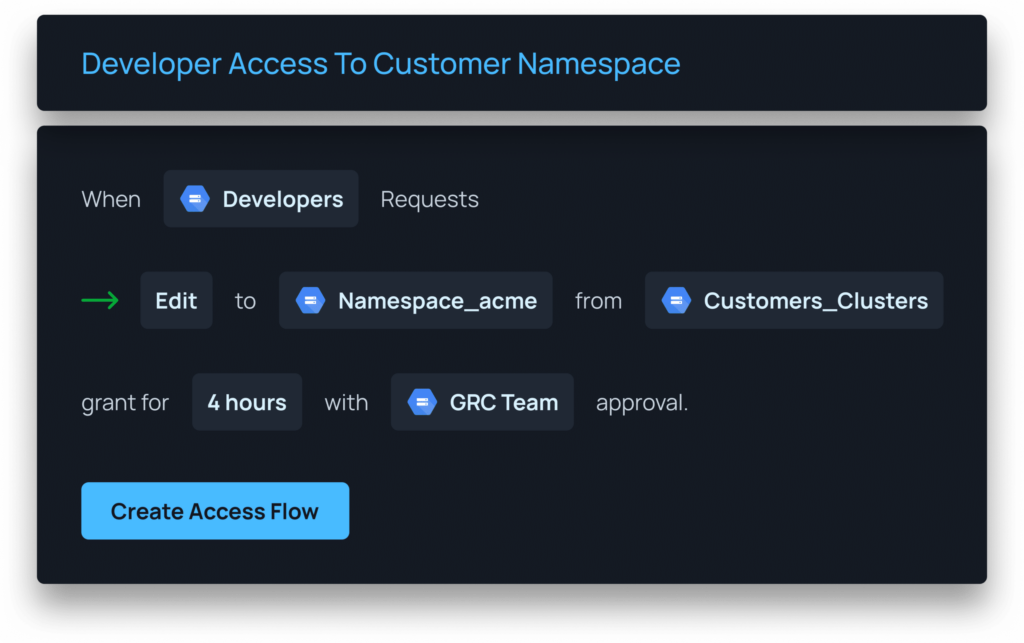
Apono perfectly complements Access Analyzer by allowing you to take the results from Analyzer and create right-size policies in a few steps:
Step 1: Enable Access Analyzer in your AWS account.
Step 2: Go to Apono and start by creating broad policies, such as access to all account data, and then enable access in your account.
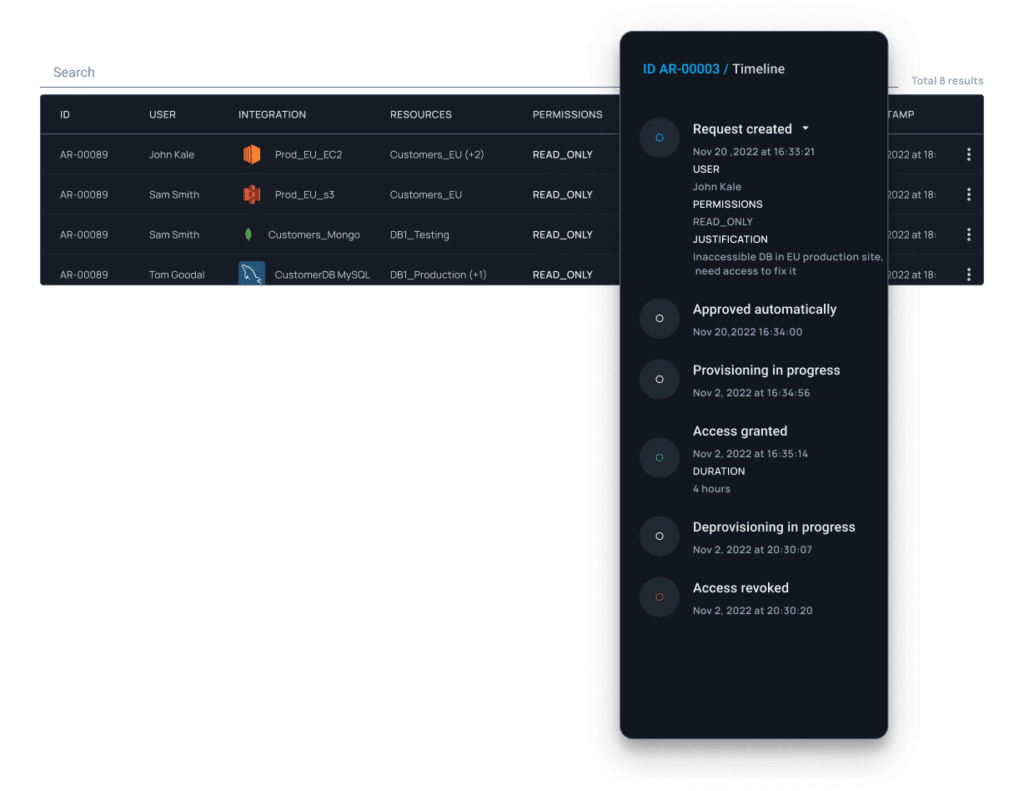
Step 3: After a certain period of time, check the Access Analyzer results to see how users utilize the access. Then, split them into two: what’s used and what’s not used.
Step 4: Now, create two workflows in Apono. The first will be based on used policies, and the other will be for just-in-time access. Then repeat the process every so often, and you’ll always be safe.
Get started with Apono for free.