RBAC vs. ABAC: Choosing the Right Access Control Model for Your Organization
It’s 9:00 AM, and your team is ready to tackle the day. But before they can start, access issues rear their ugly head. A developer can’t get into the staging server and IT is buried under a mountain of permission requests. Sounds familiar?
Employees lose up to five hours weekly on IT access issues, while IT teams spend 48% of their time handling manual provisioning. These inefficiencies cost both time and valuable progress.
So, how do you fix it? Enter Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), two powerful frameworks that streamline managing permissions.
RBAC: What is it and how does it work?
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a no-nonsense way to manage who gets access to what in your organization. Instead of juggling permissions for every individual user (which gets messy fast), you create roles based on job functions. Then, you assign permissions to those roles, not people.
Why use RBAC?
RBAC is about keeping control without wasting time or risking data loss. Want to prevent an intern from accidentally messing with your production environment? RBAC has your back.
RBAC works because it’s predictable. It reduces human error, keeps access levels consistent, and makes audits straightforward. Plus, it’s scalable. Whether you have a team of 10 or 10,000, RBAC helps you avoid access sprawl while keeping your environment secure.
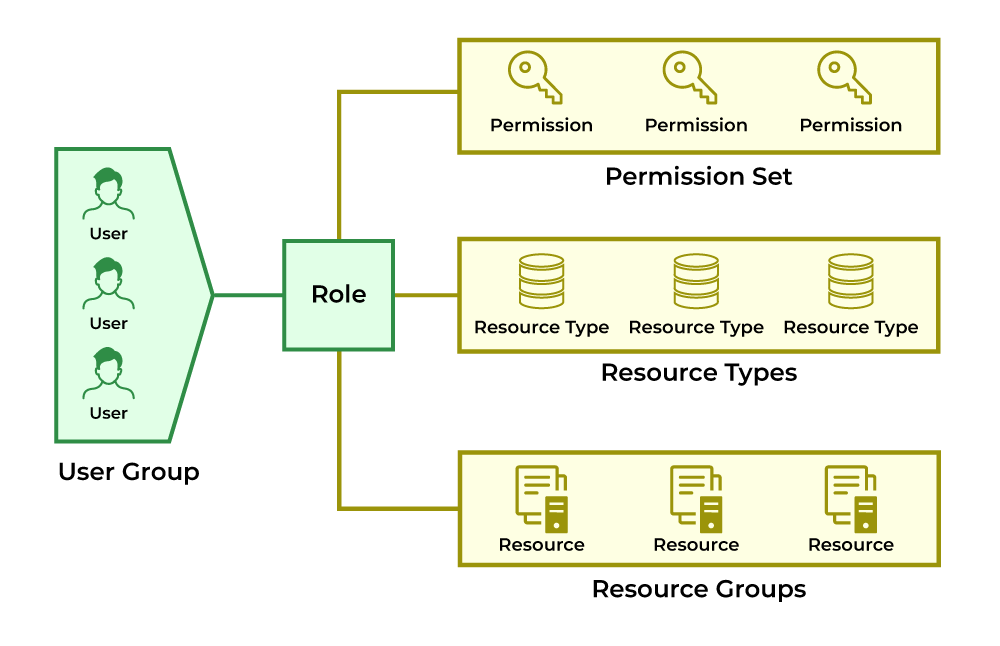
How does RBAC work?
- Define Roles: First, figure out what your team actually does. Are there engineers or incident response teams? Each role should represent a specific job function.
- Assign Permissions: Next, decide what each role needs to access. Keep it limited to the essentials—RBAC is about “need to know,” not “nice to have.”
- Assign Users to Roles: This is the easy part—just assign people the right roles. For example, a new hire in DevOps can be assigned the “Junior DevOps Engineer” role, and they’ll instantly get the correct permissions to access source code repositories, deployment pipelines, and monitoring dashboards. No tedious, one-off setups are required.
- Enforce Access: The system does the rest. It checks the user’s role before granting access, and if someone tries to step outside their permissions, they’re blocked.
ABAC: What is it, and how does it work?
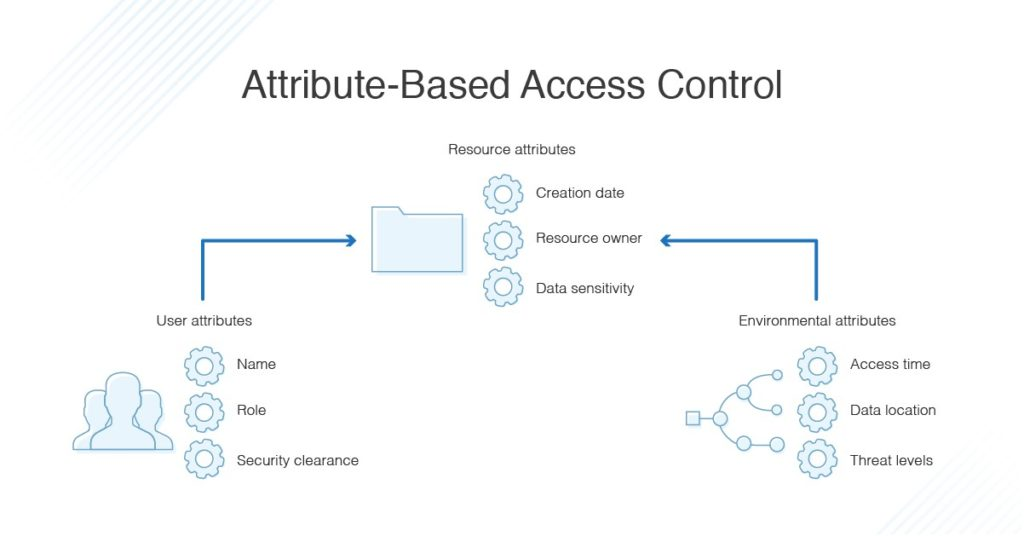
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) takes access management up a notch by adding context to permissions. Instead of just asking, “What’s your role?” ABAC asks, “Who are you? Where are you? What are you trying to do, and why?” ABAC best practices offer a more flexible and detailed approach designed for situations where a simple role doesn’t cut it.
What is ABAC used for?
ABAC shines in complex environments where access needs depend on more than just job titles. Think about healthcare systems, where a doctor might need access to patient records but only for patients they’re actively treating. Or global organizations, where access policies might depend on a user’s location, time of day, or even their device. ABAC adds these layers of nuance, ensuring access is granted under the right conditions.
How does ABAC work?
- Define Attributes: Start by identifying the relevant attributes. These could include:
- User attributes (e.g., department, clearance level)
- Resource attributes (e.g., file type, sensitivity level)
- Environmental attributes (e.g., time, location, IP address)
- Set Policies: Next, create rules that tie attributes together. For example:
- “Allow access to financial reports only if the user is in the Accounting department and the request is during business hours.”
- “Grant editing permissions to customer data if the user is a manager and on a company device.”
- Evaluate Requests: When someone tries to access a resource, the system evaluates the attributes against the defined policies. If the attributes match the rules, access is granted. If not, they’re denied.
- Enforce Dynamic Access: Unlike RBAC, which relies on static roles, ABAC decisions are made in real time. ABAC allows for much finer control over who can access what and under what circumstances.
RBAC vs. ABAC: The Pros and Cons of Each
Each model has unique strengths, and choosing the right one depends on your organization’s needs.
Pros and Cons of RBAC
Pros:
- Simple to Implement: Roles are predefined and easy to assign, making setting up RBAC nice and fast.
- Scalable: Works well for growing organizations with clear job hierarchies.
- Predictable: Access permissions are consistent and easy to audit.
- Compliant: Meets requirements for most compliance management needs and standards, like HIPAA and GDPR.
Cons:
- Limited Flexibility: RBAC can’t adapt to contextual factors like time, location, or device.
- Role Explosion: As organizations grow, the number of roles can get out of hand, complicating management.
- Static Nature: Changes to roles or permissions often require manual updates, which can slow things down.
Pros and Cons of ABAC
Pros:
- Highly Flexible: Access decisions are dynamic and consider multiple attributes, such as user, resource, and environment.
- Granular Control: Ideal for complex environments with nuanced access needs.
- Context-Aware: Supports policies based on real-time conditions, such as location or device type.
- Scalable Across Complex Systems: Works well in industries like healthcare or finance, where access needs vary widely.
Cons:
- Complex to Implement: Requires detailed planning to define attributes and policies.
- Higher Resource Needs: Real-time evaluation of attributes can demand more system resources.
- Harder to Manage: Maintaining and auditing policies can be overwhelming without proper tools.
- Steeper Learning Curve: Teams need time and expertise to understand and maintain ABAC systems.
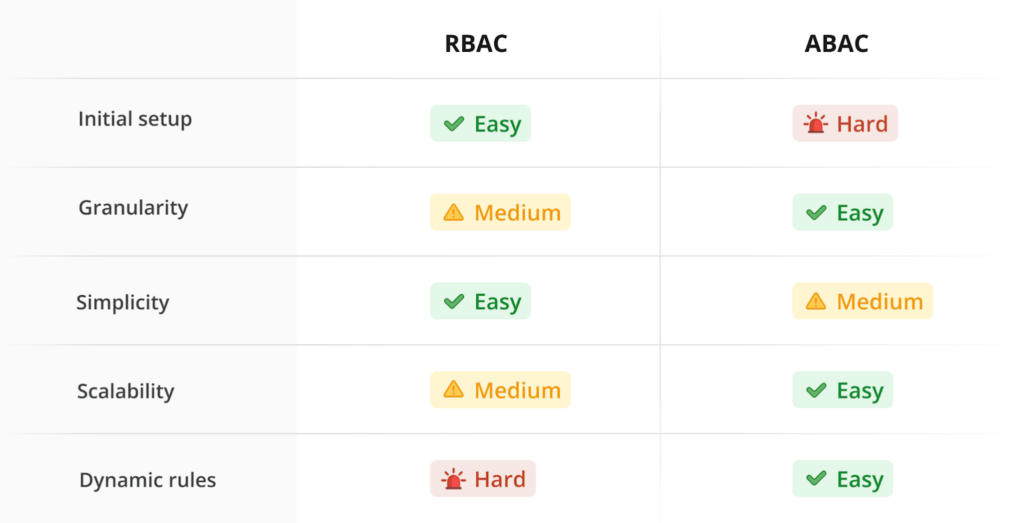
Summary Table
| Feature | RBAC | ABAC |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to set up, predefined roles | Requires detailed policy setup |
| Flexibility | Limited, based on static roles | Dynamic, context-aware |
| Scalability | Good for clear hierarchies | Best for complex environments |
| Management | Straightforward but prone to role sprawl | Complex and requires expertise |
| Performance Impact | Minimal resource demands | Higher due to real-time evaluations |
| Best Fit For | Organizations with clear, stable job roles | Dynamic, high-stakes environments |
When Should You Choose RBAC vs. ABAC?
Choosing between RBAC vs. ABAC depends on your organization’s size, complexity, and specific access control needs. Each model serves a purpose, and the best choice often depends on the context in which you operate. Both RBAC and ABAC fit into wider zero trust strategies by enforcing least privilege principles. Here’s a breakdown of when to use RBAC, ABAC, or a mix of both.
When to Use RBAC
RBAC is the better fit if:
- Your Organization Has Clear Job Roles: If your workforce operates within defined roles—like “DevOps Manager,” “Incident Responder,” or “IT Admin”—RBAC simplifies access management challenges. It’s easy to implement and scales well with structured hierarchies.
- Compliance Is a Priority: RBAC aligns seamlessly with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX. If your organization needs to demonstrate strict control over audit access, RBAC ensures consistency and traceability.
- You Need Predictability and Simplicity: Organizations with stable access requirements benefit from RBAC’s straightforward role assignments. For example, assigning employees to predefined roles is usually sufficient in a small-to-mid-sized company.
Example: A mid-sized retail company uses RBAC to manage employee access to point-of-sale systems, inventory databases, and HR portals. Employees in the “Store Manager” role get broad permissions, while “Cashiers” only access sales tools.
When to Use ABAC
ABAC is the clear choice if:
- You Operate in a Complex or Dynamic Environment: Organizations with variable access needs—where context like time, location, or device matters—thrive with ABAC’s granularity. It adapts to real-time conditions, making it ideal for global or highly regulated industries.
- You Need Context-Aware Access: ABAC’s ability to evaluate attributes such as user identity, device type, or IP address is critical for nuanced decisions. For example, only allowing access to sensitive financial data during office hours, from authorized devices, and by verified users.
- Granular Control Is Non-Negotiable: ABAC enables fine-tuned access policies that go beyond job roles. It is invaluable for sectors like healthcare, where a doctor may only access patient records they’re treating.
Example: A multinational bank adopts ABAC to grant access based on department, location, and user clearance levels. A branch manager in New York might access regional reports, while one in London is restricted to EU-specific data.
When to Use Both
In some cases, a hybrid approach makes the most sense. Many organizations use RBAC as the foundation for day-to-day operations but layer ABAC on top for more sensitive or nuanced scenarios. For instance:
- RBAC for Broad Access: Assign employees to roles for general access, like department-level tools or shared drives.
- ABAC for Sensitive Data: Implement attribute-based rules for high-risk scenarios, like accessing customer data or financial systems.
Example: A tech company uses RBAC to give engineers access to development tools while using ABAC to ensure that senior engineers can only access production servers during deployments on secure devices.
Simplifying Access Control with Apono
RBAC and ABAC each bring unique strengths to access control, and the right choice depends on your organization’s needs. RBAC offers simplicity and predictability, while ABAC delivers unmatched flexibility for dynamic environments.
Apono makes managing both RBAC and ABAC seamless. By automating access flows with features like Just-In-Time permissions and granular, self-serve controls, Apono ensures that your team stays productive without compromising security. Whether you need to simplify compliance or eliminate standing permissions, Apono integrates with your stack in minutes, helping you confidently scale access management.
Book a demo to see Apono in action today.